Interconnectivity & AI Support – Everything You Need To Know About Modern Data Centres
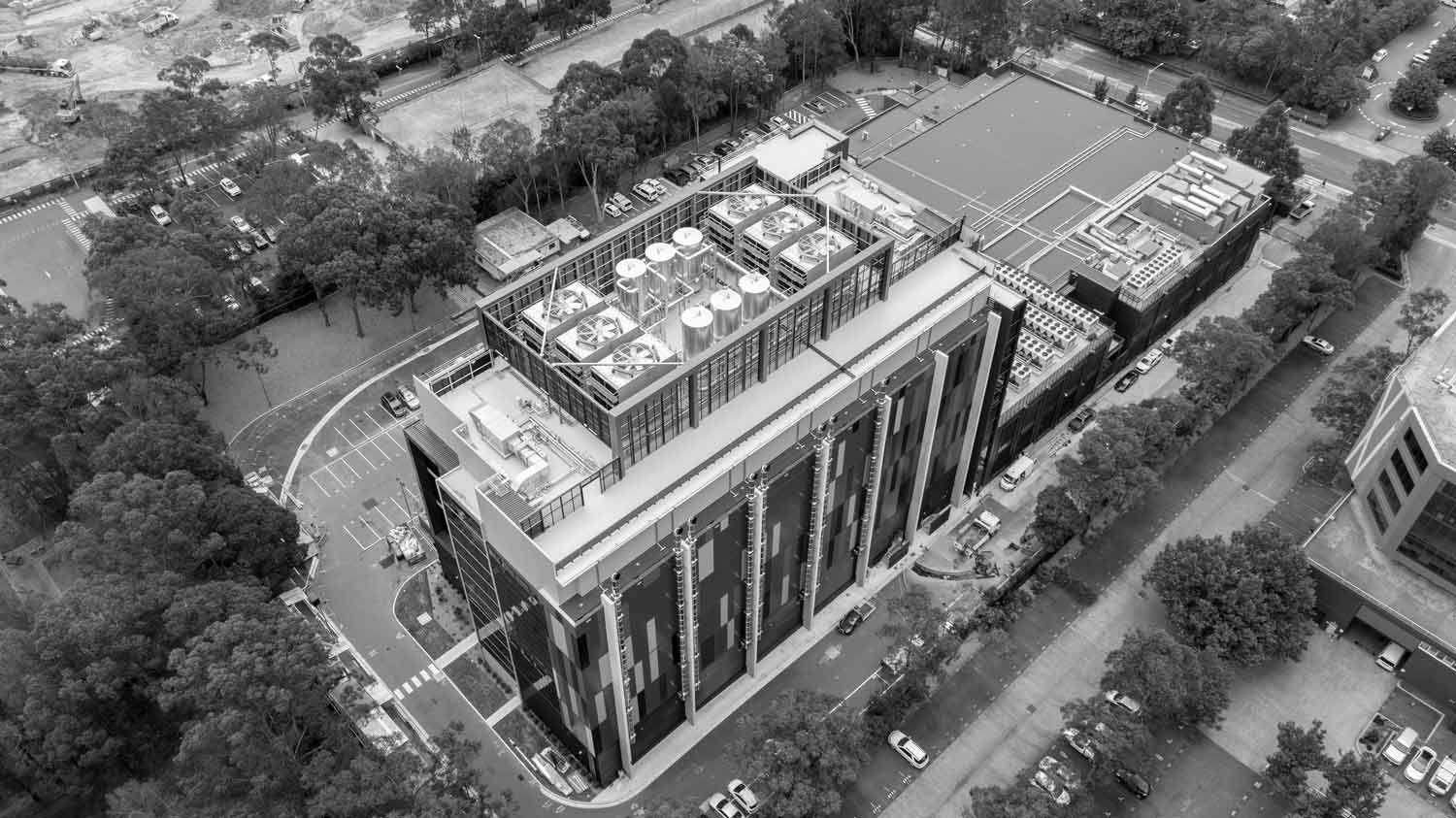

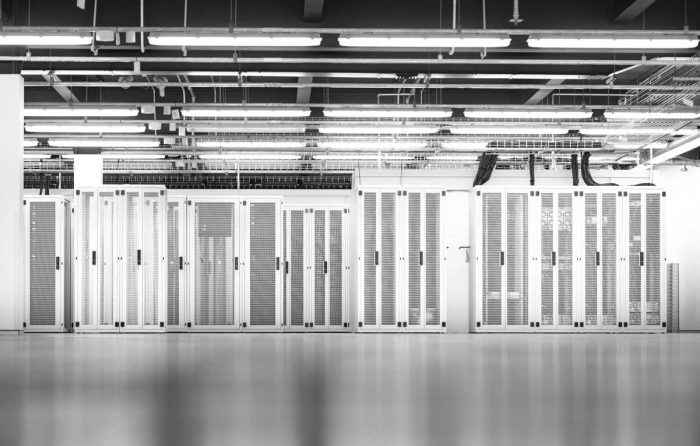
In the intricate ecosystem of a modern organisation, a data centre is a pivotal component. These dedicated facilities provide centralised hubs for businesses to house their essential IT operations and equipment, creating secure and resilient environments that support today’s cutting-edge technologies, from AI to cloud computing.
Let’s explore what data centres are used for in businesses, their components, data tiers and how they can be used to support modern pieces of technology.
Components of a data centre.
Every business has undergone a digital transformation in one way or another — from cloud storage to SAAS-based tools to boost productivity, improve accounting processes and more. However, what you might not know is that all this technology sits in data centres across the globe. Let’s break down what a data centre is and what a data centre does for a business’s operations and applications:
- Power systems – These systems are vital for the continuous operation of hosted services and for ensuring uninterrupted power supply.
- Cooling mechanisms – DCs have precision cooling capabilities that maintain an optimal environment for IT equipment, preventing overheating.
- Networking infrastructure – DCs serve as connectivity hubs and internet gateways, ensuring fast and secure data transfers across various parts of a business’s network.
- Security and surveillance – State-of-the-art security systems ensure that data integrity and infrastructure are uncompromised.
The operational framework of data centres.
If you were to ask what a data centre is, at the core, it is a masterfully designed space where various components work together smoothly. This complex infrastructure facilitates data storage and uptime of their mission-critical applications.
Data centres are the cornerstones of digital transformation, offering organisations the capability for rapid data processing, in-depth analysis and efficient distribution. Partnering with region-specific data centres also ensures that businesses strictly comply with local regulatory mandates.
Colocation is the central product of data centres. Colocation, or “Colo”, hosts a business’s IT and infrastructure in an off-site location. Businesses can rent spaces to store their servers and hard drives that are maintained by the data centre. Colo supports scalability and is an ideal solution for international businesses looking to streamline their overseas operations.
The significance of data centres.
In our evolving digital age, the relevance of data centres extends beyond infrastructure. So, what are data centres used for? Well, they are instrumental in ensuring uninterrupted business operations, fostering scalability and driving technological innovation. By streamlining processes and catalysing data-centric strategies, data centres play a quintessential role in sharpening the competitive prowess of enterprises.
The blueprint of innovation.
Aside from learning what’s in a data centre, it is also important to know how a data centre works. Data centres are intricate facilities that not only house vast amounts of information but also ensure its rapid and secure transmission.
So, how are data centres built? How does one design such complex hubs? Here’s an overview of the meticulous process of architecting a data centre and the many aspects that businesses should consider in its implementation.
Data centre tiers.
Data centre tier classifications were established by the Uptime Institute 25 years ago and have become widely regarded as the exemplary standard for rating the performance and reliability of data centres worldwide. They are made up of four tiers, each defined by specific metrics related to maintenance, power, cooling, security and fault capacity.
As each tier is progressive and built upon previous tiers, a tier will always incorporate the tiers that precede it.
- Tier 1 – A basic infrastructure design offering an uninterrupted power supply and a dedicated area for IT systems. Tier 1 provides bare bones redundancy measures, with a backup power supply in case of power outages.
- Tier 2 – Tier 2 combines the same characteristics as Tier 1, but offers additional redundancy measures for cooling and power distribution. Its components can also be removed without having to shut down the entire facility, minimising disruption and downtime.
- Tier 3 – This tier combines all characteristics of its predecessors, but with the addition of an independent and isolated infrastructure, facilitating more power resources and distribution paths.
- Tier 4 – The gold standard of data centres, containing all of the aforementioned features and capabilities with the addition of advanced security measures, high-end fire suppression systems and strict access controls to safeguard data and equipment.
Hyper-converged Infrastructure (HCI).
Hyper-converged Infrastructure represents a significant shift from traditional data centre architecture. In the past, computing, storage and networking functions all required separate hardware and systems. With HCI, you get the benefits of:
- Integrated systems – All essential functions are combined into a single, software-driven solution. This allows for ease in scaling and typically results in lower hardware costs.
- Simplified management – By consolidating systems, managing operations becomes streamlined. They are now often handled through a single interface, enhancing the efficiency of how a data centre works.
- Flexibility – HCI is inherently more flexible, letting businesses add resources as needed without overhauling the entire system.
Incorporation of modern technologies.
For data centres to remain relevant and efficient, the integration of modern technologies is paramount. This is pivotal to understanding what data centres are used for in today’s fast-paced tech environment.
- Artificial intelligence (AI) — Data centres provide powerful support to AI applications in terms of computing power, infrastructure and storage. They can also ensure scalability to meet growing demands while maintaining data security and compliance.
- Automation — What do data centres do for automation? DCs support automation applications by offering orchestration platforms and integration points that promote efficient resource and configuration management while facilitating rapid responses to changing demands — all of which are crucial for supporting various automation tasks.
- Internet of Things (IoT) — IoT devices generate vast amounts of data, which often require real-time or near-real-time processing for actionable insights. How a data centre works for IoT is by delivering the computational power needed to process and analyse data streams quickly, enabling timely decision-making.
Strategic integration into the Australian landscape.
Imagine a multinational corporation extending its reach into Australia. Given this scenario, you may wonder what data centres are for, in the context of large multinationals. By collaborating with a local sovereign data centre provider, the organisation achieves:
- Regulatory & compliance adherence – Ensuring operations fully align with Australian data regulations, thereby fostering trust and compliance.
- Strengthening local connections – Streamlined collaborations are paramount, and local partnering optimises interactions with government entities and local businesses.
- Enhanced customer experiences – Leveraging domestic data centres significantly reduces data latency, ensuring prompt service delivery and optimised experiences for Australian users.
This alignment with a local data centre provider underscores the strategic foresight of global enterprises looking to establish a robust presence in the Australian ecosystem.
Embracing a data-driven future with Macquarie Data Centres.
As the human population increases, its uptake of new and existing technologies and the importance of secure and compliant data centres will become paramount. Colocation data centres emerge as a vital component, offering organisations flexibility and scalability, while hyperscale data centres cater to expansive enterprise needs, effortlessly managing vast amounts of data. Robust data centre infrastructures in regions like Sydney, where the tech ecosystem is thriving, are becoming indispensable.
But beyond the hardware and location, it’s the assurance of compliance certifications that offers peace of mind to businesses, guaranteeing that operations meet regulatory standards. Moreover, the undeniable connectivity advantage these centres provide ensures seamless operations, making them not just a part of the digital framework but crucial linchpins. Macquarie Data Centres offer these and more. If you’re curious about our data centres and the services, feel free to reach out, and we’d be more than happy to help.